SUMMARY
Following on from a training and development package prepared and delivered for a major Telco provider Power, this document has been put together to help identify future opportu- nities for Remotely Piloted Aircraft (RPAS), in the Telecommunications sector. We aim to identify other cases around the world where efficiences have been realised by utilising RPAS technology to improve inspections and monitoring of towers.
One of our original trials for a large Telco client in Australia was utilising RPAS technology to help with defect identification of structures as well as cataloging of potential areas of interest for comparison of these issues over time. This trial leveraged a combination of manual review as well as deep learning methodologies for automated identification of defects and areas of interest.
OPPORTUNITIES
The opportunties for Drones in the Telco in- dustry are plentiful. There are situations where drones will allow data to be captured in a more efficient manner, saving time and resources that can be diverted elsewhere. This can be anything from asset inventory calculations, through to asset management and condition reporting, and antenna azimuth measure- ment, as well as RF measurements.
Drones can be used to improve the reliability of data supply through condition monitoring, and fault finding on areas where supply and faults may already be identified. There is a safety realization as elevated work platforms only need to be used for repairs/installations instead of inspections.
Leveraging additional technologies such as deep learning, and artificial intelligence will enable further savings, cost reductions and efficiencies to be realized, thereby enabling better outcomes for both customers, and Tel- co companies themselves. Lastly – telco pro- viders can utilize the data (in the form of 3D models, point clouds, and images) as a single source of truth for equipment which resides on a tower.
REGULATIONS
One of the current challenges preventing Drones from being utilised more regularly in Telco applications, is the requirement in Aus- tralia to keep the RPA within line of sight of the person conducting the operations. Typically, this limits the radius of operations to 300-400 metres, depending on the person’s eyesight, and size of the RPA itself.
Future iterations of the regulations, namely the manual of standards will allow drones to be operated under what’s called extended visual line of sight (EVLOS)
The updated extended visual line of sight reg- ulations allow for the RPA to be operated up to 1500 metres away from the relevant observer. There are 2 classes of EVLOS operations pro- vided for under the Manual of Standards.
There are additional opportunity sets to be realised in Telco surveys allowing more auto- mation.
Drones have the ability to capture a higher quality dataset reapatably, generally with more information per image/scan than tradition- al methods. Valuable analytics can then be extracted from each asset, whether that be tower, mast, or other structure.
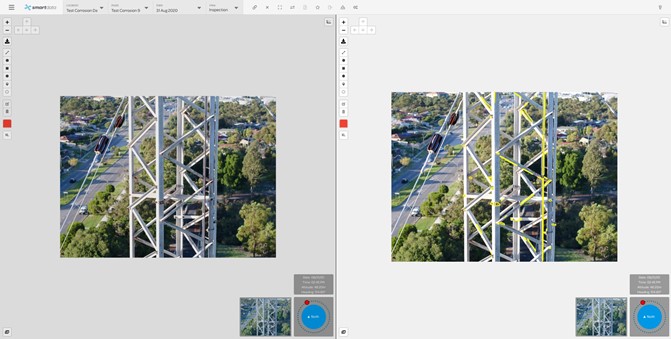
OPPORTUNITIES – TOWER INSPECTION PROGRAMSIn the past, inspection programs have been completed by riggers climbing towers, utilizing EWPs or cherry pickers to get the required inspections of towers. This is often a manual process with associated risk of people working at heights. This process is also largely subjective when it comes to data review, as one engineers view may differ from others. This is where deep learning assists decision making for telecommunication providers and infrastructure owners, as human bias can largely be removed from the model in a well trained dataset. |
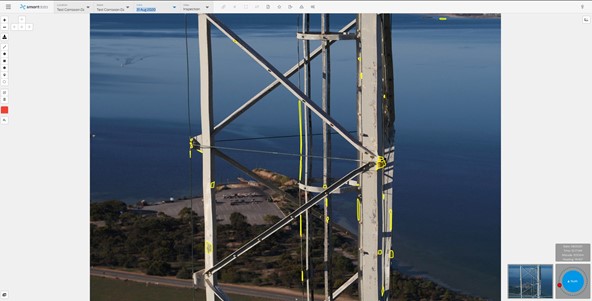 |  |
OPPORTUNITIES – DEEP LEARNING AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ANALYTICSWhere real cost savings and efficiences are able to be realised in Telco networks, is using deep-learning to identify and report on inidividual elements and record asset inventory. Deep learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence. Deep learning models perform well when the data used to train the model is of a high standard, and has been labelled correctly in the first instance. There are elements of deep learning models using re-en- forcement training among other things, but the first step to correctly deploying deep learning and data analytics is to ensure the data captured is of a sufficiently high quality. A poorly trained deep learning model will create additional challenges with false positives and incorrectly identified aspects requiring re-training.
By coupling automatic recognition of assets and inventory, as well as identification of defects on struc- tures, and repeatable flight paths, many of the challenges associated with manual inspections can be solved. Obviously large amounts of assets don’t lend themselves well to being reviewed by humans, when the datasets captured are quite large. Deep learning can be used to identify initial areas of inter- est, which can then be reviewed for accuracy. The more data that is captured, and built, the more accurate the data becomes over time. Whilst the model is being trained initially, it is important to take a longer term view (1-5 years). A correctly trained model will be able to get to a high confidence interval. The overall benefits mean that speed and quality of data capture is improved, as well as a reporting and analytics improvement. High resolution inspection data carried out by Drone, would enable planners to form accurate decisions on high priority areas for maintenance, thereby reducing potential downtime of network assets. Once the data has been captured, and the AI trained, condition based risk monitoring scores and out- puts can be created, identifying potential risks, and hazards to the network, and allowing maintenance planners to better create maintenance schedules. |
CASE STUDYSmart Data worked with a leading Telco provider in Australia to roll out an inspection program over their remote, distributed tower assets. The project realised a number of benefits particularly around safety, cost efficiences, access to data, and review and collaboration of that data across the organisation with multiple stakeholders able to access and review in a collaborative cloud platform.
|
| PROCESS | APPLICATION | BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|
| Asset inventory | • Digital cataloging • Quantity, location and quality of inventoried as- sets | • Inventory manage- ment through shared access • Data available to facilitiate effective decision making • Digital portfolio to make decisions |
| Asset Manage- ment | • Condition assessment of infrastructure with drones | • Workers safety • Decreased inspection costs and greener process • Interactive 3D Models (where re- quired) |
| Defect Identifica- tion | • Automated Corrosion Identification | • Reduced manual review • Increased worker productivity on other tasks |
OPPORTUNITIES – DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION AND ASSET DIGITISATION |
 |  |  |
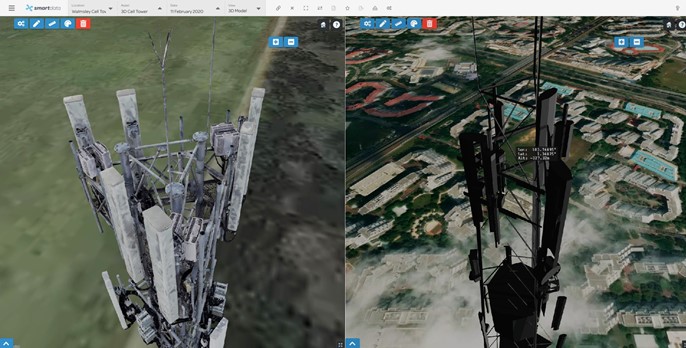
| Using a combination of technoligies, towers can now be accurately scanned to extremely high levels of accuracy, and digital twins created of an asset, moving Telco providers from paper diagrams and draw- ings of their structures, to actual, digital models available in Smartdata where assets can be tagged and highly accurate models shared within the organisation, or with third parties either who are completing work on the asset. These scans can also be used for Inventory purposes. Highly accurate models, can also be used to calculate existing space on the tower, allowing identifica- tion of revenue generating opportunities where addional antennas. These interactive models and point clouds can be navigated using our Smartdata software platform, which is also used for visualisation of inspection programs. |
OTHER OPPORTUNITIESSmartdata allows the viewing of the captured 3D model beside the BIM, or design model, to ensure installations have been conducted according to design. Telco providers are also able to then utilise these models to accurately to monitor change over time, as well as link assets back to a central asset management system.
Today – due to improvements in technology, this price is being driven down even further. Dual capture from an RGB camera and thermal camera allows defects to be identified, as shown in the image below. As each image is geo-located then individual faulty panels can easily be located, and replaced. Once an entire solar project has been scanned, it is possible to estimate efficiency losses due to faulty panels.
|
"*" indicates required fields